Banking & Financial Services
Closing the Gender Wealth Gap

OPINION
By Adelena Lopez, Inland Empire Consumer Region executive, Bank of America
While businesses are beginning to slowly and safely reopen, women workers left the workforce in disproportionate numbers during the pandemic – an issue that is set to exacerbate a growing wealth gap between women and men. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, there were 109,000 more women working than men, occupying 50.04% of positions, in December 2019. However, once the pandemic evolved, thousands of women left the workforce to accommodate responsibilities brought on by stay-at-home orders. When combining the pay gap with common workforce interruptions of parenting and caregiving – women may earn as much as $1 million less than their male counterparts by retirement age.
Thanks to a seismic shift toward increased equity for women, they are poised to move closer to true financial independence – though we know there is still a long way to go. A report from the World Economic Forum found that the gender wealth gap could take more than 250 years to close, and Bank of America’s Women Business Owner Spotlight found that access to capital remains a barrier for many women business owners.
Notably, younger women investors are twice as likely to lead their families’ financial decision-making than previous generations, according to Bank of America research. However, the research also found gender-based biases toward investors persist, making women feel they must prepare more for meetings and speak up proactively to be heard.
The good news is that we’re seeing a new generation of women changing the narrative around women and wealth. Younger women in particular are paving the way in financial empowerment and taking control of their financial lives: 75% of women under 45 manage their own finances compared to 50% of women 55 and older.
There are resources to learn more, such as Better Money Habits that offers tips around savings, retirement planning and even looking at beyond your salary to leveraging workplace benefits to your long-term financial advantage.
Here are some tips that working women can use to get on more equal financial footing:
- Start saving early to plan for eventualities – Acknowledge career interruptions, and the potential for increased healthcare costs and retirement expenses associated with living longer. Ideally, try to save at least 15% of your salary every year and take advantage of tax-efficient savings options.
- Break the taboo around money talk – Encourage more conversation between your friends and family about money management. Seek mentors and come up with the best long-term plan for you.
- Take advantage of critical wealth escalators and consider working longer – Be sure to participate in benefits like full 401(k) company matches, to help ensure long-term financial stability. Maximize Social Security and pension benefits.
Plan early and often, enlisting the guidance of financial advisor – Create a plan that matches your unique circumstances and stick to it. New research found that women feel positive about their financial advisors. Identify a financial advisor who understands women’s different financial journeys, from budgeting to saving for retirement, and can help you create a portfolio that has the potential to last your lifetime.
Banking & Financial Services
California’s Economic Horizon: Treasurer Ma’s Optimistic Forecast for the Inland Empire

State Treasurer Fiona Ma outlines key initiatives and predicts robust growth for the region, highlighting major projects and economic strategies
By Ken Alan, Freelance Writer for IEBJ
California State Treasurer Fiona Ma presented an optimistic economic forecast for the Inland Empire at the Mid-Year Banking & Financial Industry Outlook. “I spend a lot of my time traveling to all 58 counties to understand their economic development needs and match them with investors,” she explained.
Treasurer Ma highlighted her support for the Brightline West high-speed rail project, which secured $3 billion in funding from President Biden’s Bipartisan Infrastructure Bill and an additional $3.5 billion through private activity bonds (PABs). The 218-mile train, running through the median of Interstate 15, will have stations in Las Vegas, Victor Valley, Hesperia, and terminate in Rancho Cucamonga, where it will connect with the California High-Speed Rail.
While high-speed rail remains controversial due to its high construction costs, Ma argued that such systems are vital solutions to highway gridlock and the high cost of housing in major metro areas. With no significant highway projects in the planning stages, California legislators are considering electronic tolls to manage peak hour traffic. Additionally, the air travel industry continues to struggle with pilot shortages, high fuel costs, safety concerns, and customer service issues, which could be alleviated by increased competition. The persistent barriers to new housing—such as labor costs, high interest rates, and government red tape—also remain formidable.
The construction of the Brightline project is expected to take four years, aiming for completion in 2028 just in time for the Olympic Games in Los Angeles. Ma promised three years of high-paying construction jobs and mentioned plans for new affordable rental units and renovations to existing ones.
Treasurer Ma also referenced the Barstow International Gateway project (BIG) as another economic catalyst for the Inland Empire. Though not directly involved, she noted that the railroad company BNSF had purchased 4,000 acres on the west side of Barstow to develop a major transloading center for international freight from the ports of Los Angeles. This initiative is expected to significantly reduce truck traffic on Southern California freeways and boost San Bernardino County’s economy.
Treasurer Ma oversees a state budget of $3.7 trillion. During the first two years of the pandemic, California realized surpluses of $46 billion and $96 billion, respectively. However, in the third year, the state faced a $50 billion deficit due to layoffs in tech companies, declines in commercial leases, and reductions in individual and corporate tax revenue.
“Our state heavily relies on personal income tax, corporate tax, and sales taxes,” Ma added, noting that as of May, personal income taxes were up $1.4 billion over projections and corporate taxes had risen by $752 million.
Ma invited business leaders to explore the California State Treasurer’s website (www.treasurer.ca.gov) to learn more about state programs that support economic prosperity, including Cal Savers, the Scholarship 529, and CalABLE for disabled workers.
She is currently collaborating with a Blue Ribbon Commission to provide banking services to residents unable to afford traditional banking. Ma emphasized that California’s quality of life remains a competitive advantage over lower-tax states with laws she described as unfriendly to women, minorities, teachers, and doctors. She also noted the high interest from investors in the state.
The Mid-Year Outlook featured a panel discussion with industry leaders on the current and future states of finance. William Wang, MBA, a cash flow expert, encouraged business leaders to consider the opportunity costs against high interest rates, suggesting that a 5% rate change should not significantly impact businesses with a solid capital use strategy. Ursula Garrett, CPA, advised business owners to maintain accurate records to avoid audits and recommended consulting a CPA if contacted by the IRS. Krisante Gunewardena from RE/MAX Diamond Bar noted a recent reduction in lease rates, suggesting it’s an opportune time for office sector investments.
The event was hosted by the Inland Empire Regional Chamber of Commerce at Riverside City Hall’s Grier Pavilion on Thursday, June 6.
Banking & Financial Services
Rate Changes are Looming: Follow Long-Term Game Plan for Winning Capital Decisions

Four key strategies for borrowing during interest-rate uncertainty
By Greg Martinez-Miller
While basketball fans everywhere are following NBA schedules, business owners are tracking the 2024 Fed meeting schedule. But just as true hoops enthusiasts know that game strategy is comprised of more than three-point shots, so should business owners remember that interest rates aren’t the only factor for long-term success. Last December, the Fed said that it expected to cut rates, which are at a 22-year high, three times in 2024. Yet when the central bank met in March, it left rates unchanged, saying it didn’t want to jeopardize lower inflation and healthy economic growth.
So, when the Federal Open Market Committee meets again on April 30-May 1, anticipation will be high. Prognosticators are on every channel, wondering whether the central bank will keep its 5.25-5.5% target rate unchanged again, or if it will announce the first of its three cuts. And if it does, observers ask, how could lower rates impact growth in the U.S. economy?
As a commercial banker who has watched the interest rate scoreboard over the past 16 years, here’s my advice from the sidelines: Stick to your long-term game plan. Put your company in a position to win the balance-sheet game when it comes to the cost of capital.
Here are my four key strategies from my dogeared playbook to keep your head in the game:
1. See the court
Do not focus on interest rates alone for your capital strategy. You need to be aware of other negotiated factors when funding your company’s financial future. Besides interest rates, other terms — loan maturity, advance rates, and guarantees — can offer important value. Many times, it makes good strategic sense to pivot from the interest rate toward other terms to advance your company’s medium- and long-term game plan.
2. Do not overreact to the officials
The Fed is like an economic referee, making calls to control the economy’s pace. Do not lose your cool when the whistle blows. Three rate reductions are still expected this year, but when the central bank plans to make that call, no one knows – yet.
3. Manage the clock
Think about timing when it comes to borrowing. When rates dip, you might consider making a few key borrowing moves to fund some crucial projects and wait to fund other projects later in the game. Consider the purpose of the debt on your balance sheet. Would your company benefit from having a mix of floating and fixed rates? This may allow you to hedge and still potentially benefit from low floating rates, while also maintaining certainty for longer-term, fixed rates.
4. Stick with your game plan
When rates do change, do not throw out your playbook. Instead, call a time out and consult with your banker or interest rate risk advisor to help ensure your borrowing decisions match your company’s long-term plans and goals for continued growth and success.
If you do not need capital, do not borrow just to lock in a lower rate. Interest rates should not be the driving factor when making borrowing decisions. Borrow when you need to; have a good reason for it.
Remember, interest rate changes will always interrupt the flow of your game. But your goal is to ensure that your financial future is deliberate – not purely defensive, based on the ebb and flow of interest rates.
Greg Martinez-Miller is the commercial banking leader for Wells Fargo in Inland Empire. Based in Ontario, Martinez-Miller leads a team of commercial relationship managers in Riverside and San Bernardino Counties. The views expressed present the opinions of the author on prospective trends and related matters in middle market banking trends as of this date, and do not necessarily reflect the views of Wells Fargo & Co., its affiliates and subsidiaries.
Banking & Financial Services
2024 Inland Empire Financial Summit: A Milestone in Economic Empowerment

Uniting Leaders and Innovators for a Thriving Economic Future in Southern California’s Inland Region
The Inland Empire Regional Chamber of Commerce proudly announces the resounding success of the 2024 Financial Industry Update, a landmark event that convened key figures in California’s financial sector. Held on January 18, 2024, at the Ontario International Airport Authority Conference Center, this summit marked a significant moment for economic empowerment and collaboration in the region.
California State Treasurer Fiona Ma, the keynote speaker, expressed her admiration for the region’s financial community: “As State Treasurer, I find constant inspiration in California’s vibrant financial community. The 2024 Financial Industry Update event highlighted not only the dynamic Inland Empire economic landscape but also emphasized the crucial role of collaboration and forward-thinking in our sector. The meaningful discussions and connections formed here reflect our collective dedication to fostering a resilient and prosperous financial future for California. Proud to contribute to this vital conversation, I eagerly anticipate witnessing the positive impacts of our shared efforts unfold statewide.”
Ivo A. Tjan, Chairman, President & CEO of CommerceWest Bank, shared his enthusiasm: “It was an honor to be invited as a guest speaker. The IE has a strong, diversified, and robust business community that is an important economic engine for California. CommerceWest Bank is excited to continue supporting local businesses in the IE and expanding our footprint.”
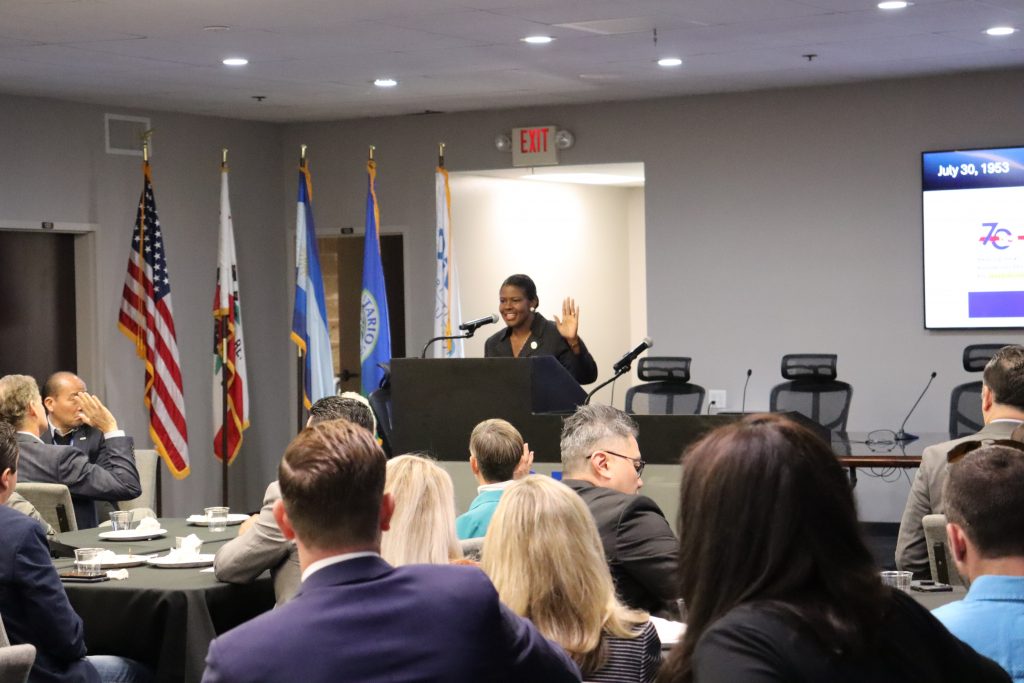
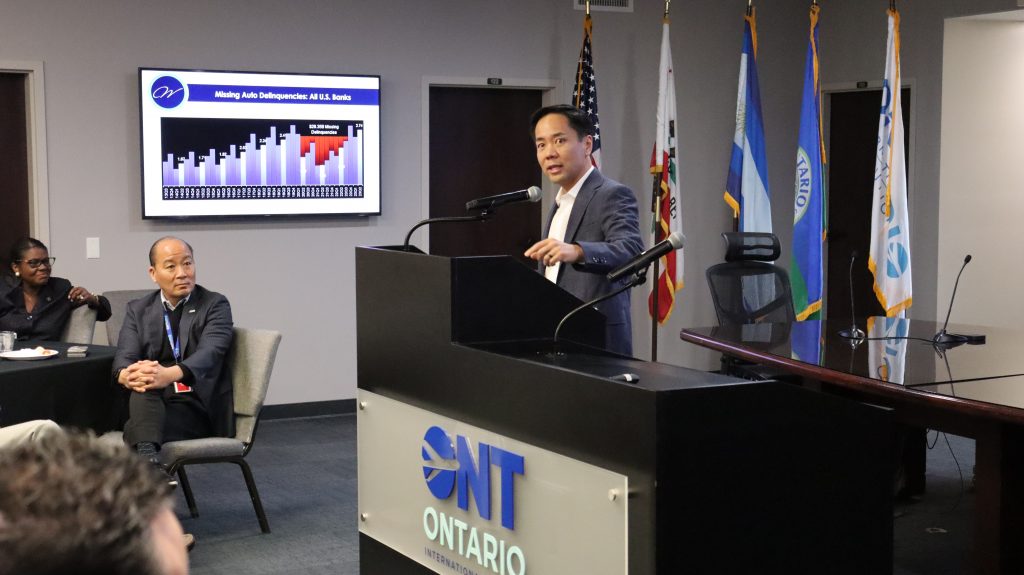
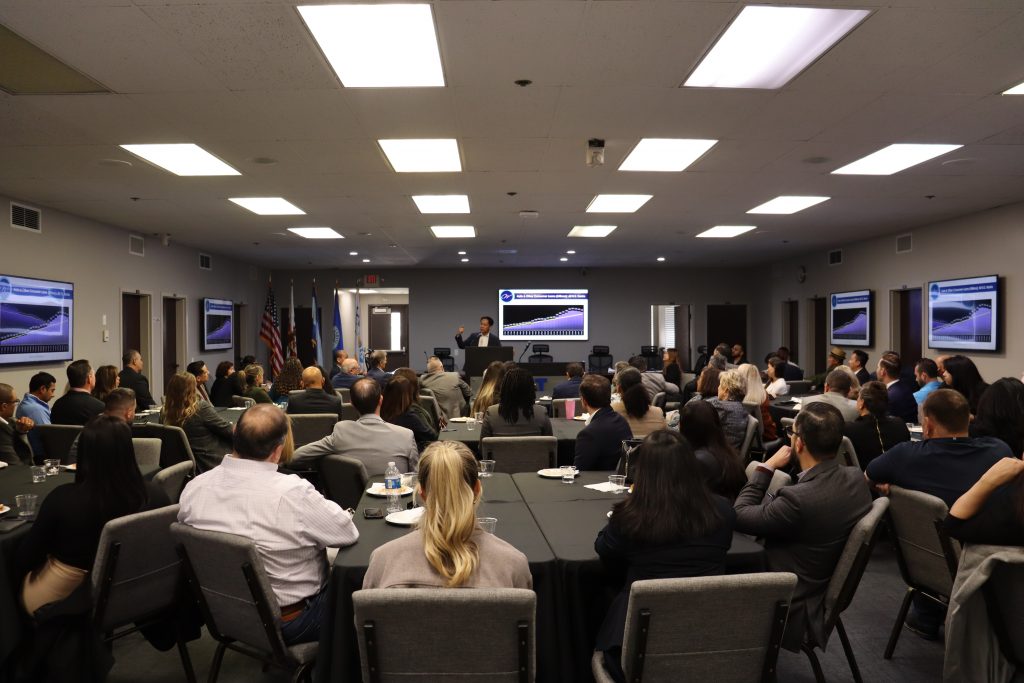
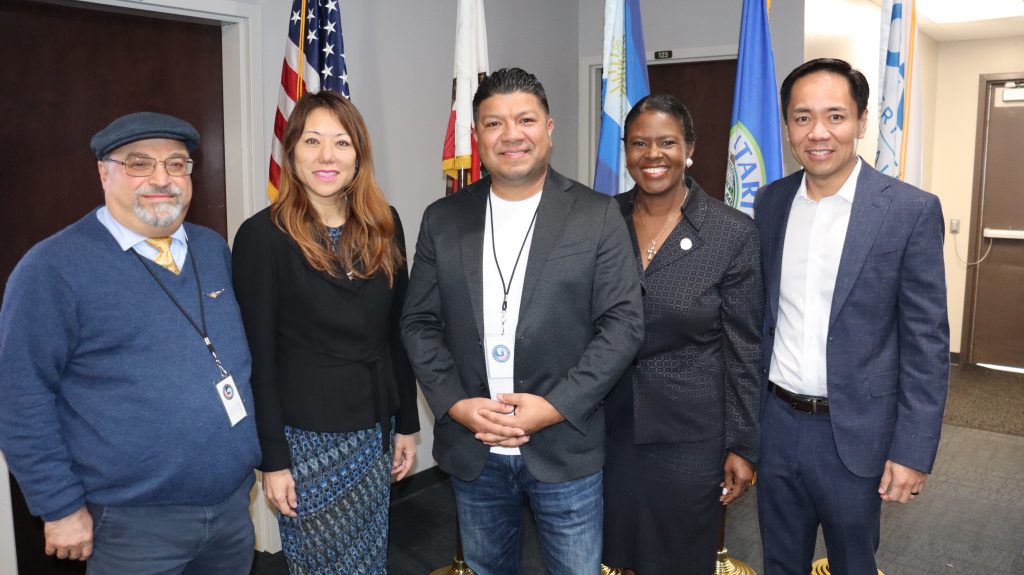






Hilda Kennedy, President & Founder of AmPac Business Capital, praised the event’s impact: “The Inland Empire Chamber did it again! They brought relevant, high-level content to help businesses plan for success in 2024. State Treasurer Fiona Ma and Ivo Tjan were exceptional! I agree with State Treasurer Ma, the Inland Empire region will save California.”
Christina Scranage, Business Development Manager at Keystone Advanced Solutions, reflected on the event’s value: “Grateful for the insightful conference today! The speakers provided valuable information, making me optimistic about our community’s economic outlook. Huge thanks to everyone involved for such an informative and helpful event!”
The event was highlighted by the participation of industry leaders who provided invaluable insights into the region’s economic landscape. The Financial Industry Update served as a crucial platform for networking, knowledge sharing, and exploring the challenges and opportunities facing the financial sector in the Inland Empire and beyond.
For more information about the event and the Inland Empire Regional Chamber of Commerce, visit www.iechamber.org.
-

 Opinion1 month ago
Opinion1 month agoSurge in Unemployment Among California Youth Linked to Minimum Wage Hikes
-

 Commercial Real Estate Transactions3 weeks ago
Commercial Real Estate Transactions3 weeks agoSRS Real Estate Partners Announces Record-Breaking $6.15 Million Ground Lease Sale of a New Construction Chick-fil-A Property in Murrieta, California
-

 Health & Wellness3 weeks ago
Health & Wellness3 weeks agoBuddha Bars: A Mother’s Innovative Solution to Healthy Snacking
-
By Press Release1 week ago
California Employment Expansion Continues But Still Trails Nation